Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Sato, Isamu*; Maeda, Koji
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2017/00
Electrochemical corrosion behavior under salt water in a type 304L stainless steel used to a part of BWR core materials was investigated to evaluate the possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence for the fuel assemblies which experienced seawater exposure in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) accident. Especially, focusing on the upper end plug part having the 304L SS crevice structure, measurement of repassivation potential for crevice corrosion (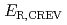 ) were carried out using the crevice test pieces fabricated by 304L SS plates. From the results,
) were carried out using the crevice test pieces fabricated by 304L SS plates. From the results, 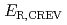 was lower than the spontaneous potential (
was lower than the spontaneous potential ( ) when the conditions of 2500 ppm chloride ion concentration at over 50
) when the conditions of 2500 ppm chloride ion concentration at over 50  C or that of 2500 ppm at over 80
C or that of 2500 ppm at over 80  C, which are included in the SFP water quality conditions. Therefore, in the 304L SS parts of the 1F fuel assemblies that experienced seawater exposure, there is a possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence.
C, which are included in the SFP water quality conditions. Therefore, in the 304L SS parts of the 1F fuel assemblies that experienced seawater exposure, there is a possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence.
Shizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki; Maeda, Koji
no journal, ,
The upper plug of a fuel rod used for the spent fuel pool (SFP) of Unit 4 in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant (1F) consists of Zircaloy-2 bolt and SUS304L nut, and it forms the screw-gap structure. Therefore, when seawater left in this gap structure by a seawater injection after an accident, crevice corrosion might occur. It may have an influence on the integrity of a fuel assembly stored in common pool. In this study, the systematic determining the repassivation potential for crevice corrosion of SUS304L and Zircaloy-2 samples. From the result, SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen indicates the tendency of corrosion to progress at 50 C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm. SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen and SUS304L/Zircaloy-2 clearance specimen show the tendency not to corrode at 80
C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm. SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen and SUS304L/Zircaloy-2 clearance specimen show the tendency not to corrode at 80 C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm.
C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm.